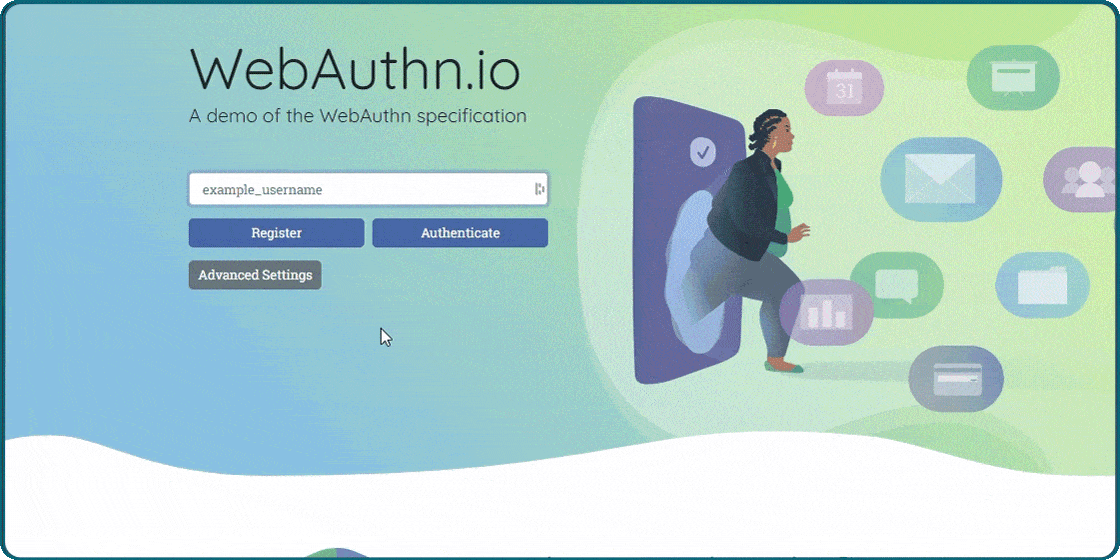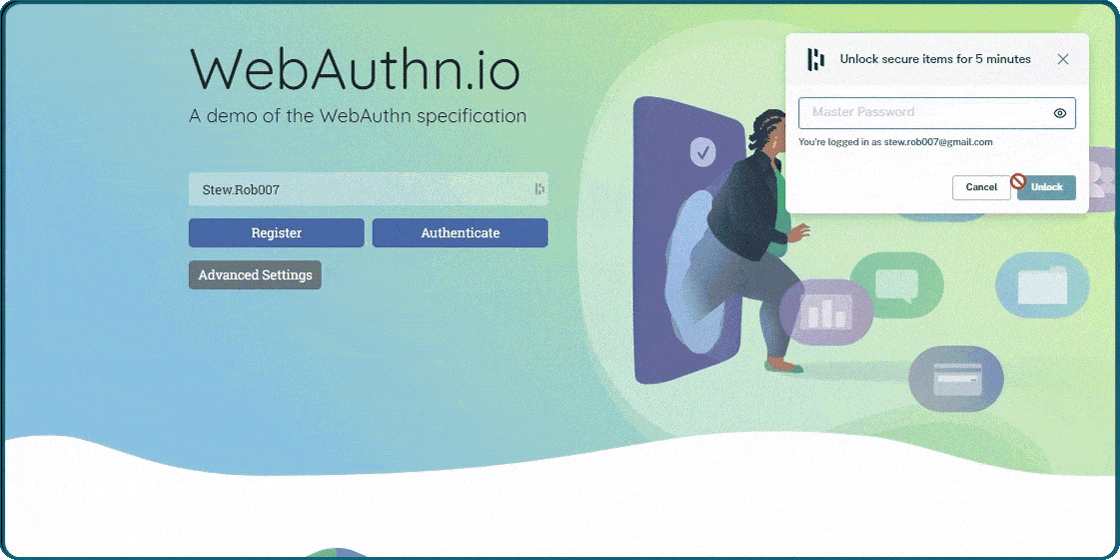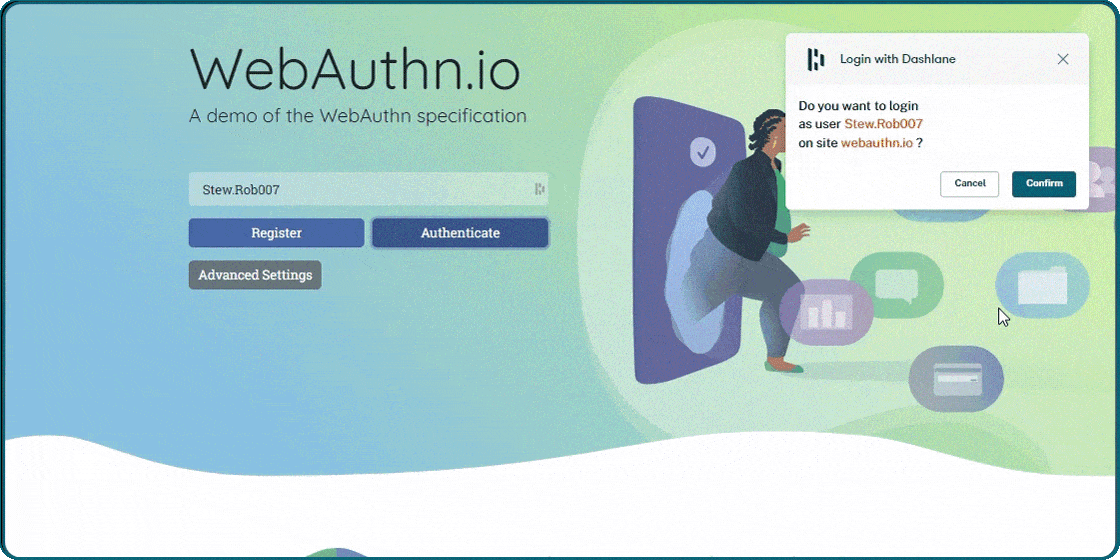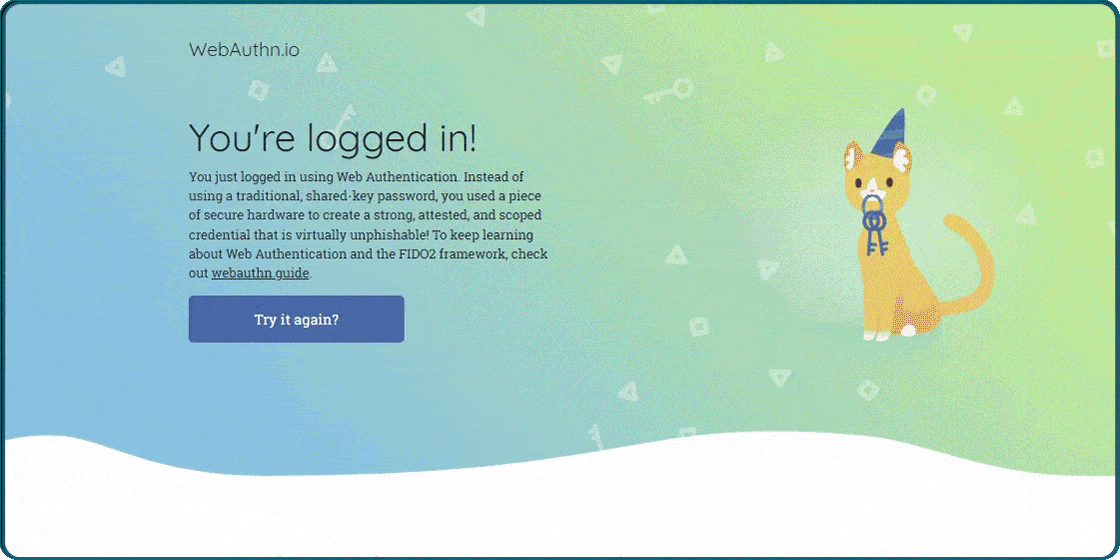
When i saw that Dashlane would support passkeys i thought that was interesting. I did not understand how it would work. You can see in the picture how it works. You have to enter Dashlane master password to use passkeys. Passkeys was supposed to get rid of passwords. It is not very bad because you only have to remember one password. Passkeys works much better with Windows Hello and a fingerprint reader.